Photomotor response data analysis approach to assess chemical neurotoxicity with the zebrafish embryo
Main Article Content
Abstract
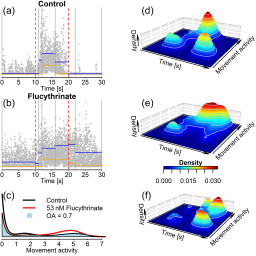
The photomotor response (PMR) of zebrafish embryos, a light pulse-triggered undirected movement, is known to be altered by neuroactive chemicals. Here, we developed an approach for data analysis of the distribution of PMR movement activities along the time axis; differences between treatment and respective controls are expressed by an aggregated value integrating the time-resolved density of the movement parameter as a measure for a chemically elicited PMR effect. Logistic concentration-PMR effect relationships were modeled for neuroactive test compounds with different modes of action (acetylcholinesterase inhibition, activation and inhibition of voltage-gated sodium channels); 50% effect concentrations (EC50) were in the low to medium μM range (EC50 < 10 μM for flucythrinate, esfenvalerate, azinphos-methyl, propoxur; EC50 > 10 μM for tricaine). Modulation of movement activities in different phases of the PMR (i.e., “fingerprint”) by neuroactive test compounds varied across concentrations, showing that mode of action-specific PMR fingerprints are also concentration-dependent. Above concentrations causing 10% lethality (LC10; 48 h), 3,4-dichloroaniline caused movement inhibition. This substance presumably is not neuroactive; its effect on the PMR therefore is considered a secondary toxic effect. Quantitative morphological examinations of chemically exposed embryos showed that malformations occurred only above PMR effect concentrations, indicating that changes in the PMR were not due to such indirect effects. The PMR assay will provide a useful measure in ecotoxicological risk assessment of neuroactive chemicals with zebrafish embryos and could potentially be used to infer acute fish toxicity levels from PMR effect concentrations of neurotoxic compounds.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is appropriately cited (CC-BY). Copyright on any article in ALTEX is retained by the author(s).
Attili, S. and Hughes, S. M. (2014). Anaesthetic tricaine acts preferentially on neural voltage-gated sodium channels and fails to block directly evoked muscle contraction. PLoS One 9, e103751. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0103751
Basnet, R. M., Zizioli, D., Taweedet, S. et al. (2019). Zebrafish larvae as a behavioral model in neuropharmacology. Biomedicines 7, 23. doi:10.3390/biomedicines7010023
Belanger, S. E., Rawlings, J. M. and Carr, G. J. (2013). Use of fish embryo toxicity tests for the prediction of acute fish toxicity to chemicals. Environ Toxicol Chem 32, 1768-1783. doi:10.1002/etc.2244
Bradbury, S. P., Carlson, R. W., Henry, T. R. et al. (2008). Toxic responses of the fish nervous system. In R. T. Di Giulio and D. E. Hinton (eds.), The Toxicology of Fishes. CRC Press. doi:10.1201/9780203647295
Brox, S., Seiwert, B., Haase, N. et al. (2016). Metabolism of clofibric acid in zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio) as determined by liquid chromatography-high resolution-mass spectrometry. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 185-186, 20-28. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2016.02.007
Buckingham, S. D. and Ali, D. W. (2004). Sodium and potassium currents of larval zebrafish muscle fibres. J Exp Biol 207, 841-852. doi:10.1242/jeb.00839
Busquet, F., Strecker, R., Rawlings, J. M. et al. (2014). OECD validation study to assess intra- and inter-laboratory reproducibility of the zebrafish embryo toxicity test for acute aquatic toxicity testing. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 69, 496-511. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2014.05.018
Copmans, D., Meinl, T., Dietz, C. et al. (2016). A KNIME-based analysis of the zebrafish photomotor response clusters the phenotypes of 14 classes of neuroactive molecules. J Biomol Screen 21, 427-436. doi:10.1177/1087057115618348
Coutts, C. A., Patten, S. A., Balt, L. N. et al. (2006). Development of ionic currents of zebrafish slow and fast skeletal muscle fibers. J Neurobiol 66, 220-235. doi:10.1002/neu.20214
D’Amora, M. and Giordani, S. (2018). The utility of zebrafish as a model for screening developmental neurotoxicity. Front Neurosci 12, 976. doi:10.3389/fnins.2018.00976
de Brujin, M. H., Labrada, L. A., Smyth, A. J. et al. (1993). A comparative study of diagnosis by the polymerase chain reaction and by current clinical methods using biopsies from colombian patients with suspected leishmaniasis. Trop Med Parasitol 44, 201-207.
Ducharme, N. A., Peterson, L. E., Benfenati, E. et al. (2013). Meta-analysis of toxicity and teratogenicity of 133 chemicals from zebrafish developmental toxicity studies. Reprod Toxicol 41, 98-108. doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2013.06.070
Embry, M. R., Belanger, S. E., Braunbeck, T. A. et al. (2010). The fish embryo toxicity test as an animal alternative method in hazard and risk assessment and scientific research. Aquat Toxicol 97, 79-87. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2009.12.008
Fukuto, T. R. (1990). Mechanism of action of organophosphorus and carbamate insecticides. Environ Health Perspect 87, 245-254. doi:10.1289/ehp.9087245
Gauthier, P. T. and Vijayan, M. M. (2018). Nonlinear mixed-modelling discriminates the effect of chemicals and their mixtures on zebrafish behavior. Sci Rep 8, 1999. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-20112-x
Glaberman, S., Padilla, S. and Barron, M. G. (2017). Evaluating the zebrafish embryo toxicity test for pesticide hazard screening. Environ Toxicol Chem 36, 1221-1226. doi:10.1002/etc.3641
Gruber, S. J. and Munn, M. D. (1998). Organophosphate and carbamate insecticides in agricultural waters and cholinesterase (ChE) inhibition in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 35, 391-396. doi:10.1007/s002449900393
Hanneman, E. and Westerfield, M. (1989). Early expression of acetylcholinesterase activity in functionally distinct neurons of the zebrafish. J Comp Neurol 284, 350-361. doi:10.1002/cne.902840303
Herzsprung, P., Weil, L. and Niessner, R. (1992). Measurement of bimolecular rate constants k(i) of the cholinesterase inactivation reaction by 55 insecticides and of the influence of various pyridiniumoximes on k(i). Int J Environ an Ch 47, 181-200. doi:Doi 10.1080/03067319208027028
Jacob, E., Drexel, M., Schwerte, T. et al. (2002). Influence of hypoxia and of hypoxemia on the development of cardiac activity in zebrafish larvae. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 283, R911-917. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00673.2001
Klüver, N., König, M., Ortmann, J. et al. (2015). Fish embryo toxicity test: Identification of compounds with weak toxicity and analysis of behavioral effects to improve prediction of acute toxicity for neurotoxic compounds. Environ Sci Technol 49, 7002-7011. doi:10.1021/acs.est.5b01910
Klüver, N., Vogs, C., Altenburger, R. et al. (2016). Development of a general baseline toxicity QSAR model for the fish embryo acute toxicity test. Chemosphere 164, 164-173. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.08.079
Knöbel, M., Busser, F. J., Rico-Rico, A. et al. (2012). Predicting adult fish acute lethality with the zebrafish embryo: Relevance of test duration, endpoints, compound properties, and exposure concentration analysis. Environ Sci Technol 46, 9690-9700. doi:10.1021/es301729q
Kokel, D., Bryan, J., Laggner, C. et al. (2010). Rapid behavior-based identification of neuroactive small molecules in the zebrafish. Nat Chem Biol 6, 231-237. doi:10.1038/nchembio.307
Kokel, D., Cheung, C. Y., Mills, R. et al. (2013a). Photochemical activation of trpa1 channels in neurons and animals. Nat Chem Biol 9, 257-263. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1183
Kokel, D., Dunn, T. W., Ahrens, M. B. et al. (2013b). Identification of nonvisual photomotor response cells in the vertebrate hindbrain. J Neurosci 33, 3834-3843. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.3689-12.2013
Lammer, E., Carr, G. J., Wendler, K. et al. (2009a). Is the fish embryo toxicity test (FET) with the zebrafish (Danio rerio) a potential alternative for the fish acute toxicity test? Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 149, 196-209. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2008.11.006
Lammer, E., Kamp, H.G., Hisgen, V. et al. (2009b). Development of a flow-through system for the fish embryo toxicity test (FET) with the zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxicol In Vitro 23, 1436-1442. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2009.05.014
Legradi, J., el Abdellaoui, N., van Pomeren, M. et al. (2015). Comparability of behavioural assays using zebrafish larvae to assess neurotoxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22, 16277-16289. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3805-8
Nagel, R. (2002). Dart: The embryo test with the zebrafish Danio rerio – A general model in ecotoxicology and toxicology. ALTEX 19, Suppl 1, 38-48. https://www.altex.org/index.php/altex/article/view/2125
OECD (2013). Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2. OECD Publishing, Paris. doi:10.1787/9789264203709-en
OECD (2019). Test No. 203: Fish, Acute Toxicity Test. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2. OECD Publishing, Paris. doi:10.1787/9789264069961-en
Ogungbemi, A., Leuthold, D., Scholz, S. et al. (2019). Hypo- or hyperactivity of zebrafish embryos provoked by neuroactive substances: A review on how experimental parameters impact the predictability of behavior changes. Environ Sci Eur 31, 88. doi:10.1186/s12302-019-0270-5
Reif, D. M., Truong, L., Mandrell, D. et al. (2016). High-throughput characterization of chemical-associated embryonic behavioral changes predicts teratogenic outcomes. Arch Toxicol 90, 1459-1470. doi:10.1007/s00204-015-1554-1
Rombough, P. (2002). Gills are needed for ionoregulation before they are needed for o2 uptake in developing zebrafish, Danio rerio. J Exp Biol 205, 1787-1794. doi:10.1242/jeb.205.12.1787
Russom, C. L., Bradbury, S. P., Broderius, S. J. et al. (1997). Predicting modes of toxic action from chemical structure: Acute toxicity in the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Environ Toxicol Chem 16, 948-967. doi:10.1002/etc.5620160514
Russom, C. L., LaLone, C. A., Villeneuve, D. L. et al. (2014). Development of an adverse outcome pathway for acetylcholinesterase inhibition leading to acute mortality. Environ Toxicol Chem 33, 2157-2169. doi:10.1002/etc.2662
Saeed, A. I., Sharov, V., White, J. et al. (2003). Tm4: A free, open-source system for microarray data management and analysis. Biotechniques 34, 374-378. doi:10.2144/03342mt01
Scholz, S., Fischer, S., Gündel, U. et al. (2008). The zebrafish embryo model in environmental risk assessment – Applications beyond acute toxicity testing. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 15, 394-404. doi:10.1007/s11356-008-0018-z
Scholz, S., Sela, E., Blaha, L. et al. (2013). A European perspective on alternatives to animal testing for environmental hazard identification and risk assessment. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 67, 506-530. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2013.10.003
Selderslaghs, I. W., Hooyberghs, J., De Coen, W. et al. (2010). Locomotor activity in zebrafish embryos: A new method to assess developmental neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicol Teratol 32, 460-471. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2010.03.002
Selderslaghs, I. W., Hooyberghs, J., Blust, R. et al. (2013). Assessment of the developmental neurotoxicity of compounds by measuring locomotor activity in zebrafish embryos and larvae. Neurotoxicol Teratol 37, 44-56. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2013.01.003
Sobanska, M., Scholz, S., Nyman, A. M. et al. (2018). Applicability of the fish embryo acute toxicity (FET) test (OECD 236) in the regulatory context of registration, evaluation, authorisation, and restriction of chemicals (REACH). Environ Toxicol Chem 37, 657-670. doi:10.1002/etc.4055
Soderlund, D. M. and Bloomquist, J. R. (1989). Neurotoxic actions of pyrethroid insecticides. Annu Rev Entomol 34, 77-96. doi:10.1146/annurev.en.34.010189.000453
Strähle, U., Scholz, S., Geisler, R. et al. (2012). Zebrafish embryos as an alternative to animal experiments – A commentary on the definition of the onset of protected life stages in animal welfare regulations. Reprod Toxicol 33, 128-132. doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2011.06.121
Teixido, E., Kießling, T. R., Krupp, E. et al. (2019). Automated morphological feature assessment for zebrafish embryo developmental toxicity screens. Toxicol Sci 167, 438-449. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfy250
Venables, W. N. and Ripley, B. D. (2002). Modern Applied Statistics with S. Statistics and Computing. New York, NY, USA: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-21706-2